Common MySQL Issues: Set root user password and solve the access denied error


Starting with MySQL can be a bumpy road. Many beginners face common roadblocks that can feel frustrating and confusing. This guide breaks down some of the most frequent issues and provides simple, step-by-step solutions to get you back on track. Let's solve these problems together 🚀
A common initial setup issue is not being able to log in to the MySQL server or accidentally logging in with no password. This is a major security risk and a problem you must fix immediately.
You run sudo mysql and it gives you immediate access without asking for a password. This means your root user has no password set, leaving your database completely exposed. 🚩
sudo mysql'your_new_password' with a secure, unique password.ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'your_new_password';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;ALTER USER is used to change user authentication details. FLUSH PRIVILEGES reloads the user permissions, making the new password active right away. mysql -u root -pThis is a classic issue. You're trying to connect but are hit with an "Access denied" message. This usually means the username, password, or host you're using is incorrect.
Your command mysql -u myuser -p results in an Access denied error. This could be due to a wrong password, an incorrect username, or the user not having permission to connect from your location (Host).
To troubleshoot this, you need to see exactly what users and hosts exist on your MySQL server.
root user (using the password you just set) and run the following query to see all available users and their allowed hosts:SELECT User, Host FROM mysql.user;'root'@'localhost'). Double-check the spelling of the username and the host. GRANT privilege), as they can manage other users.SELECT User, Host FROM mysql.user WHERE Grant_priv = 'Y';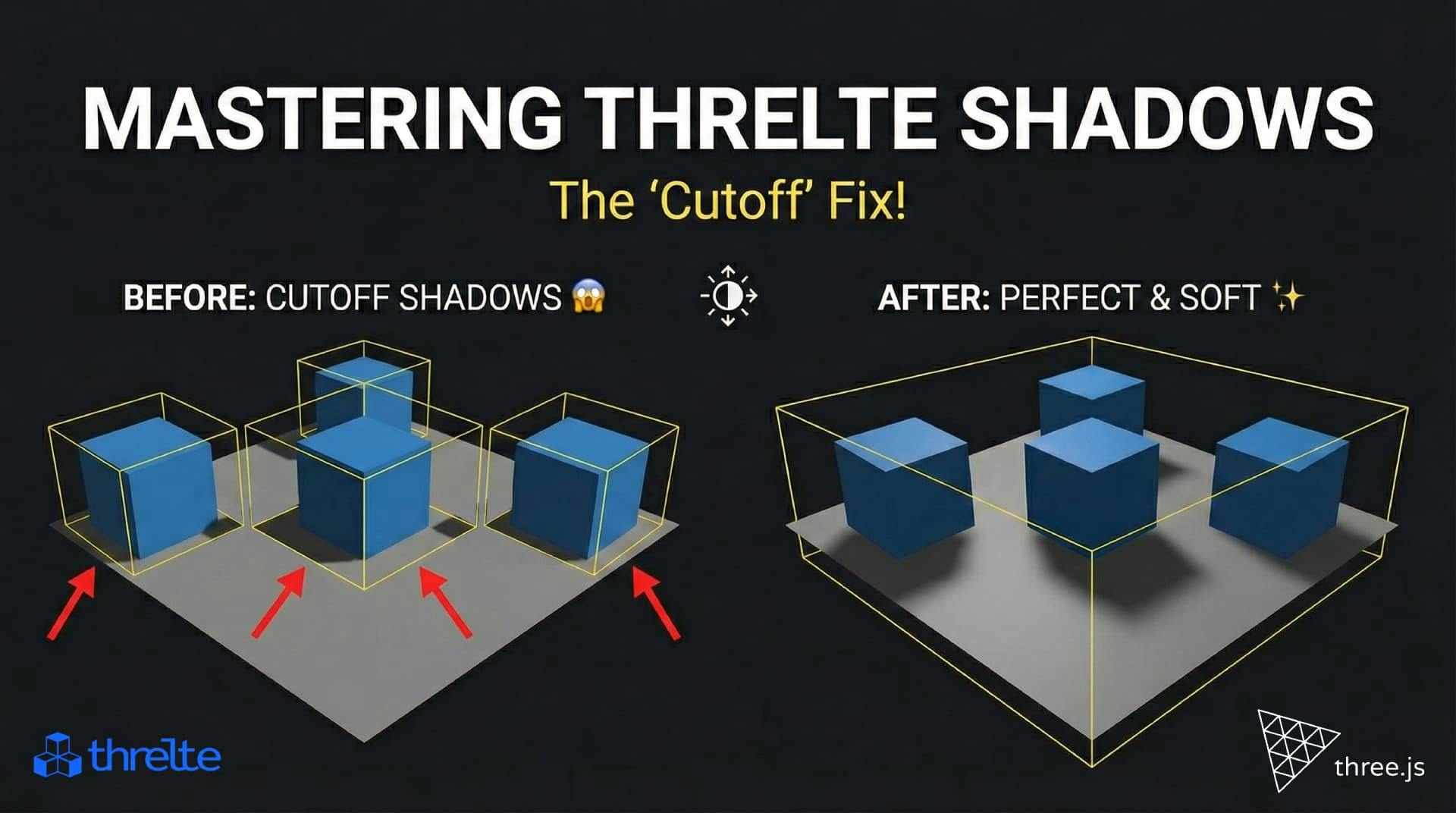
Shadows disappearing in your Threlte or Three.js scene? It’s a frustum issue. Learn how to visualize the shadow box and fix clipping instantly with this guide.

What happens when you create a DocType in Frappe? We break down the .json, .js, and .py files generated by the framework and how to use them.

Confused by Shopify's lack of a database? 🤯 Learn how Shopify stores your theme data, from simple Settings to complex Metafields. Perfect for devs moving from WP/Laravel.